PPT Introduction to Fungi PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2001302
Fungal cell structure • Yeasts (unicellular, budding) • Molds (hyphae, mycelia, spores) • Dimorphs (both) Pathogenesis Toxins: produced, but not relevant to human infections Disease from: Bulk of organisms Immune response to them or their byproducts. 2 Overview of fungal infections
Fungal Cell Structure. Fungi Hyphae with Septa Stock Vector Illustration of biological
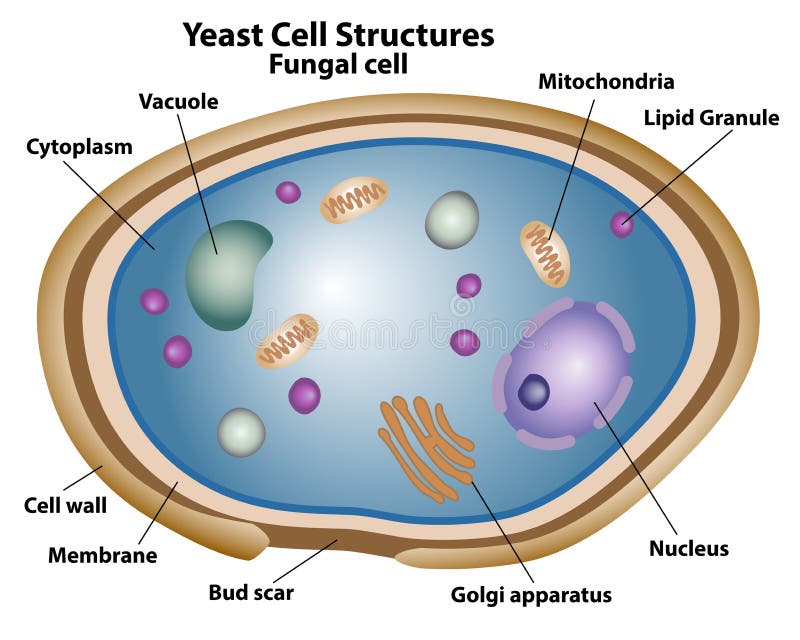
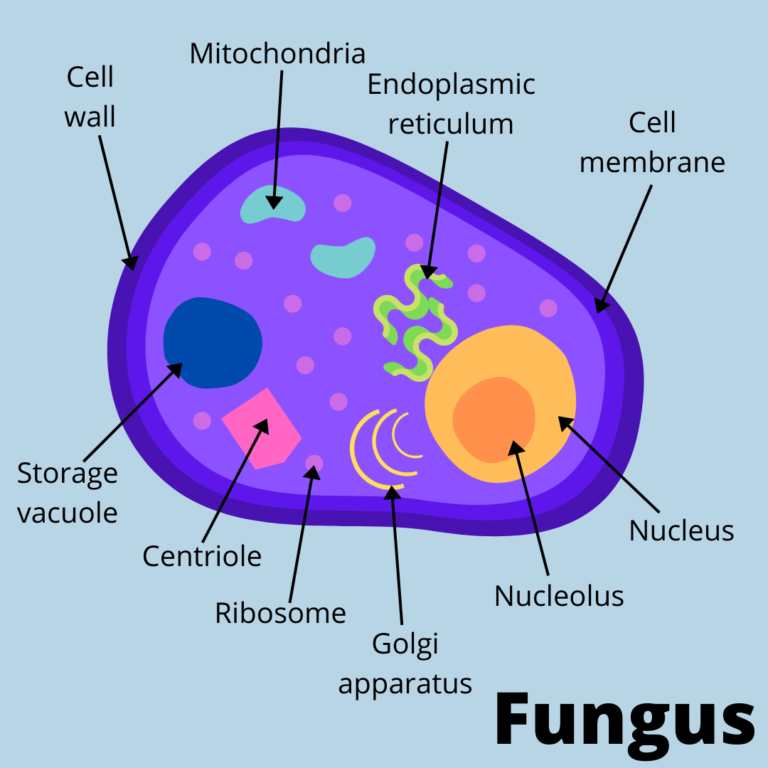
Fungi on the Phylogenetic Tree of Life. Fungi are a monophyletic group of eukaryotic heterotrophs that is closely related to animals. As eukaryotes, their cells contain a nucleus, mitochondria, and a complex system of internal membrane including the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus. Unlike plant cells, fungal cells do not have.
Fungi Structure Diagram
The composition of fungal cell walls is relatively simple and includes substances not typically found in animal and plant hosts (e.g., chitin). On this basis, it may be possible to identify pathogen-specific molecular targets from investigations of the biosynthesis of fungal wall components.

Types of Cells Biology Dictionary
Cell Structure and Function. Fungi are eukaryotes, and as such, have a complex cellular organization. As eukaryotes, fungal cells contain a membrane-bound nucleus. The DNA in the nucleus is wrapped around histone proteins, as is observed in other eukaryotic cells. A few types of fungi have structures comparable to bacterial plasmids (loops of.
Fungi As Basic Fungal Cell and Multicellular Fungus Structure Outline Diagram Stock Vector
Cell Structure and Function. Fungi are eukaryotes, and as such, have a complex cellular organization. As eukaryotes, fungal cells contain a membrane-bound nucleus. The DNA in the nucleus is wrapped around histone proteins, as is observed in other eukaryotic cells. A few types of fungi have structures comparable to bacterial plasmids (loops of.

Fungi........
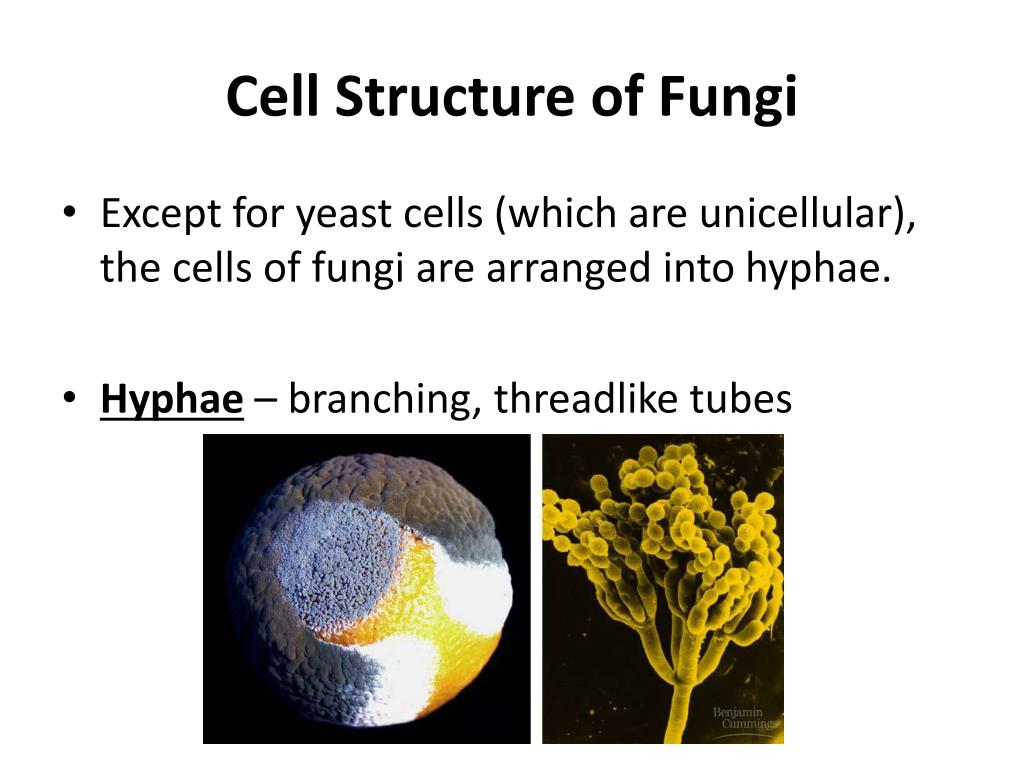
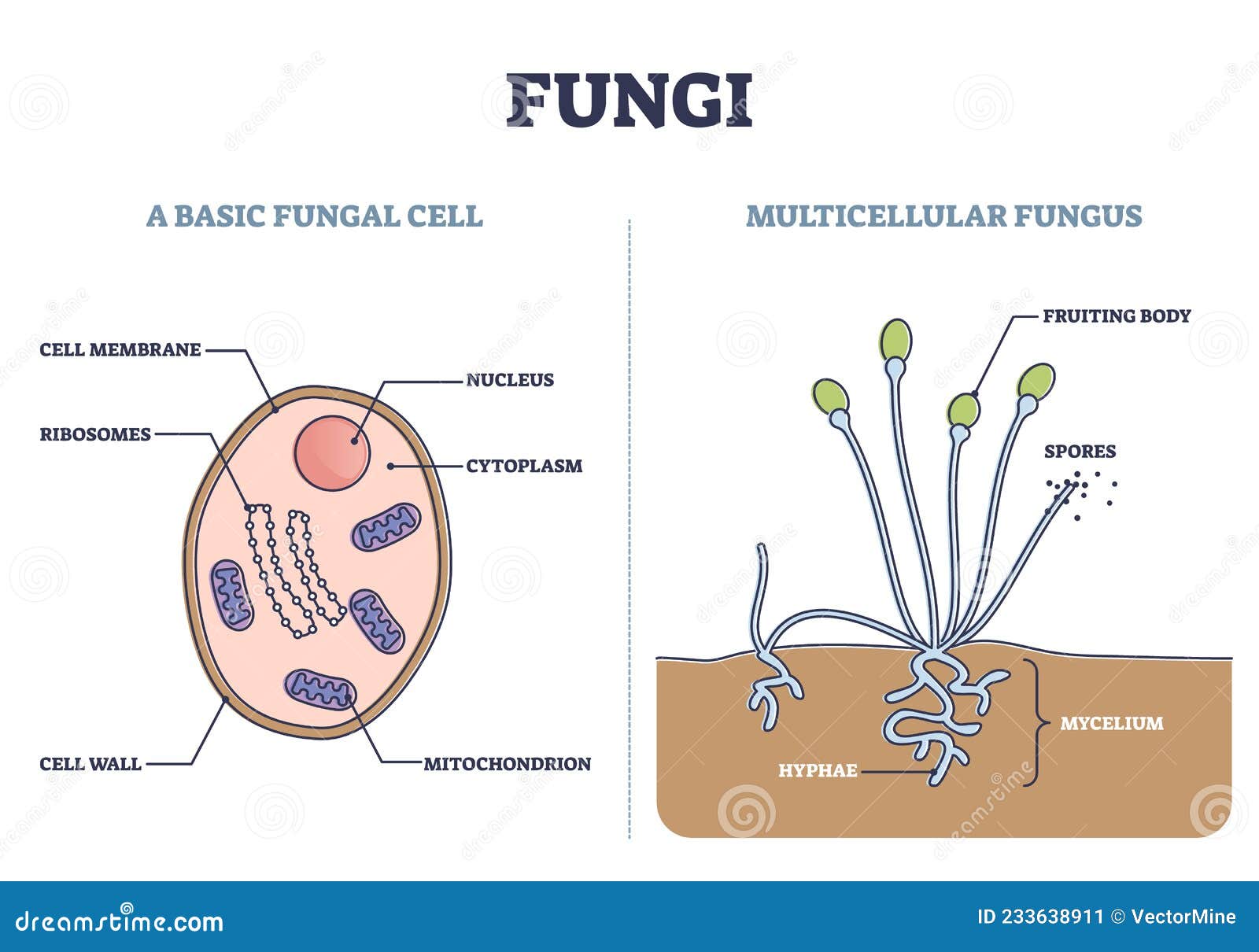
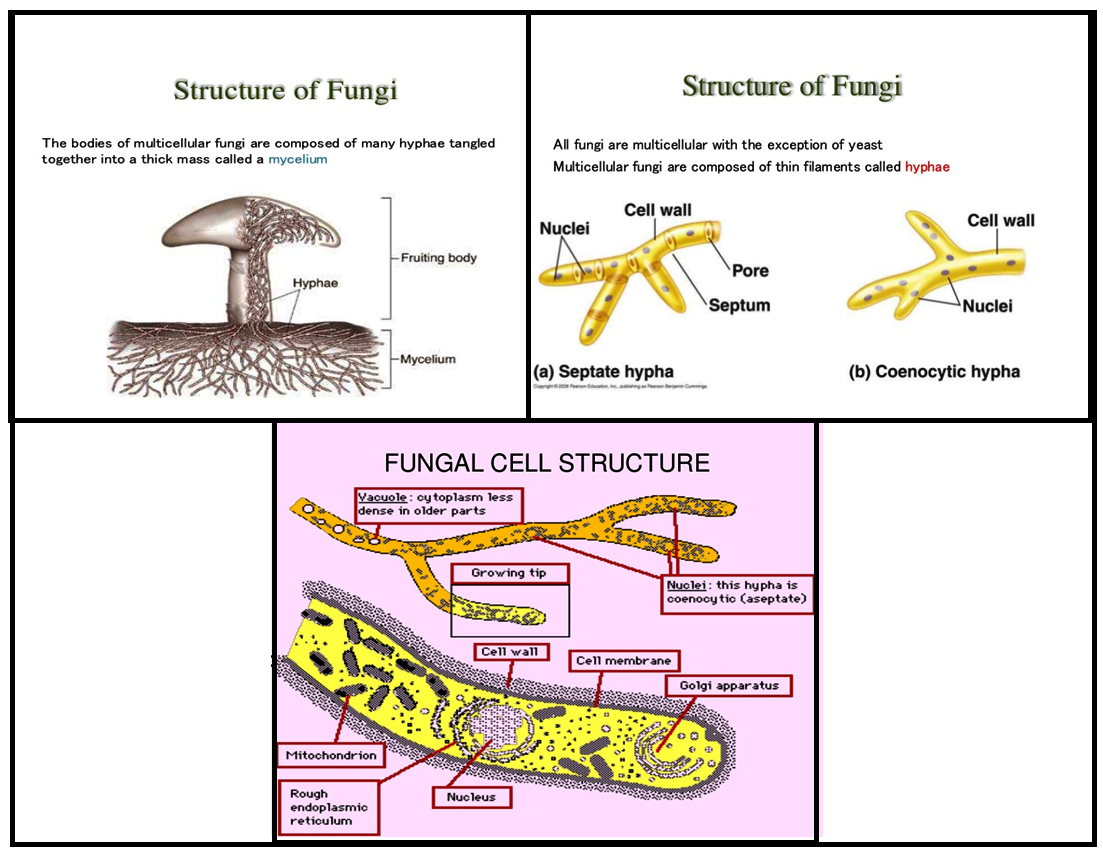
Structure of Fungi. Except for yeasts, which grow as single cells, most fungi grow as thread-like filaments, like those s hown in Figure below. The filaments are called hyphae (singular, hypha). Each hypha consists of one or more cells surrounded by a tubular cell wall. A mass of hyphae make up the body of a fungus, which is called a mycelium.
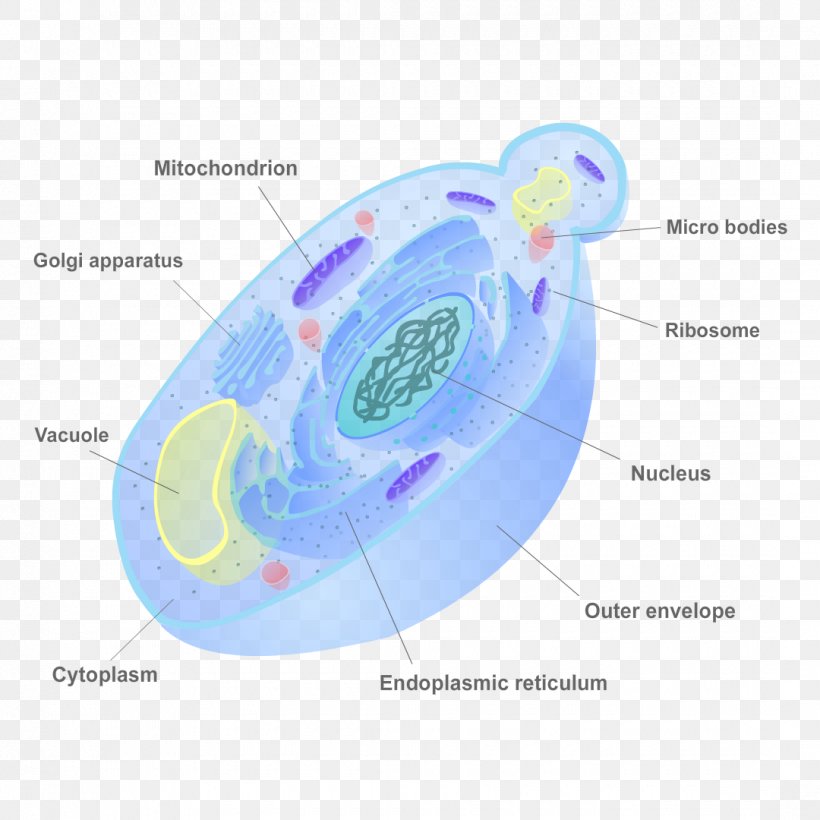
Fungus Cell Wall Yeast Biology, PNG, 1080x1080px, Fungus, Biology, Cell, Cell Wall, Chitin
The diagram below shows the ultrastructure of a typical yeast cell: Bacterial cells Bacterial cells have a more simple structure compared to animal, plant and fungal cells and are.
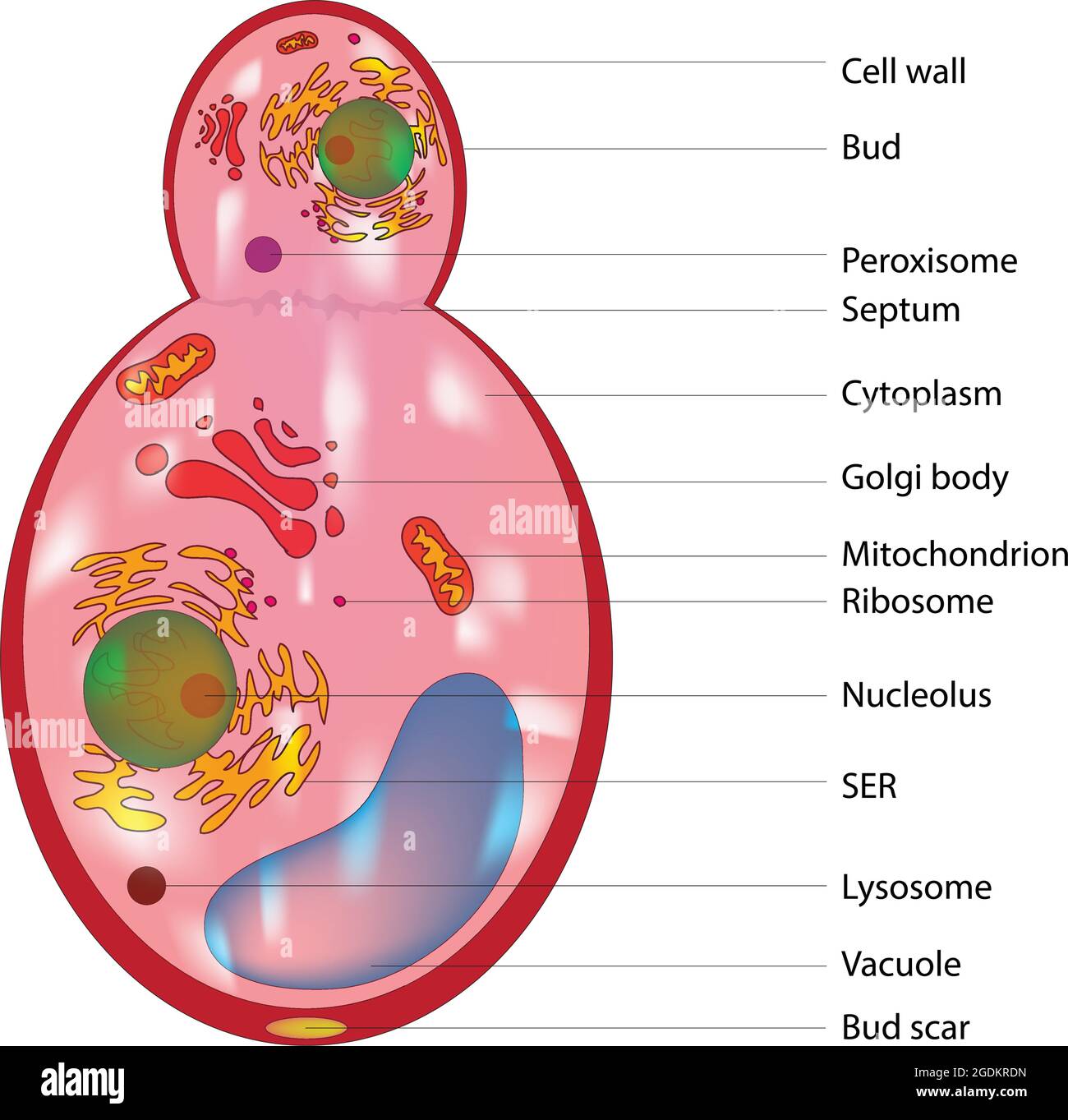
Divisione delle cellule fungine Immagini Vettoriali Stock Alamy
Cell Structure and Function. Fungi are eukaryotes and as such have a complex cellular organization. As eukaryotes, fungal cells contain a membrane-bound nucleus. A few types of fungi have structures comparable to the plasmids (loops of DNA) seen in bacteria. Fungal cells also contain mitochondria and a complex system of internal membranes.

Kingdom Fungi In Detail Biology Blog
In this context, we will discuss the structure of fungi by looking into the diagram and morphological features of both yeasts and moulds. Content: Fungal Cell Structure Characteristics Ultrastructure Structure of Yeasts Structure of Molds Distinguishing Characteristics of Fungi Fungal cells show resemblance to both plant and animal cells.
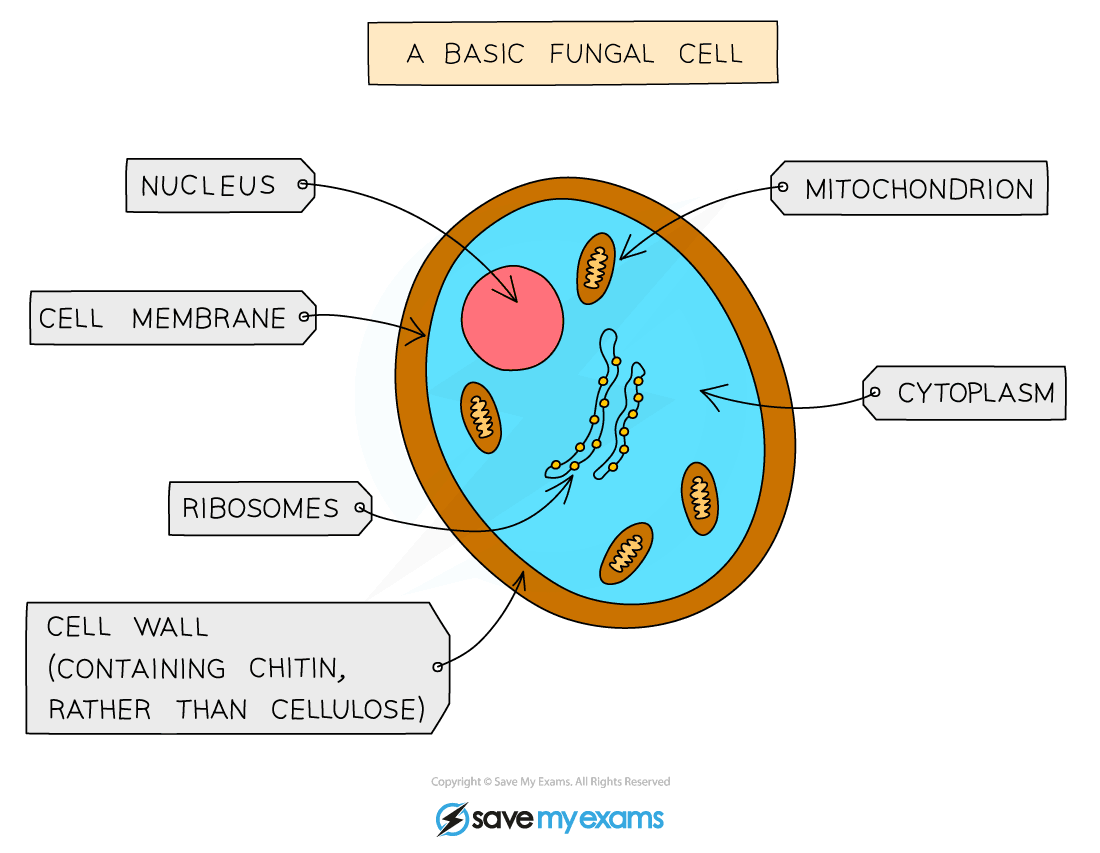
Eukaryotic Organisms Fungi & Protoctists Gidemy Class Notes
A typical fungus consists of a mass of branched, tubular filaments enclosed by a rigid cell wall.The filaments, called hyphae (singular hypha), branch repeatedly into a complicated, radially expanding network called the mycelium, which makes up the thallus, or undifferentiated body, of the typical fungus.The mycelium grows by utilizing nutrients from the environment and, upon reaching a.
Biology KINGDOM FUNGI
Cell Structure and Function Fungi are eukaryotes, and as such, have a complex cellular organization. As eukaryotes, fungal cells contain a membrane-bound nucleus. The DNA in the nucleus is wrapped around histone proteins, as is observed in other eukaryotic cells.
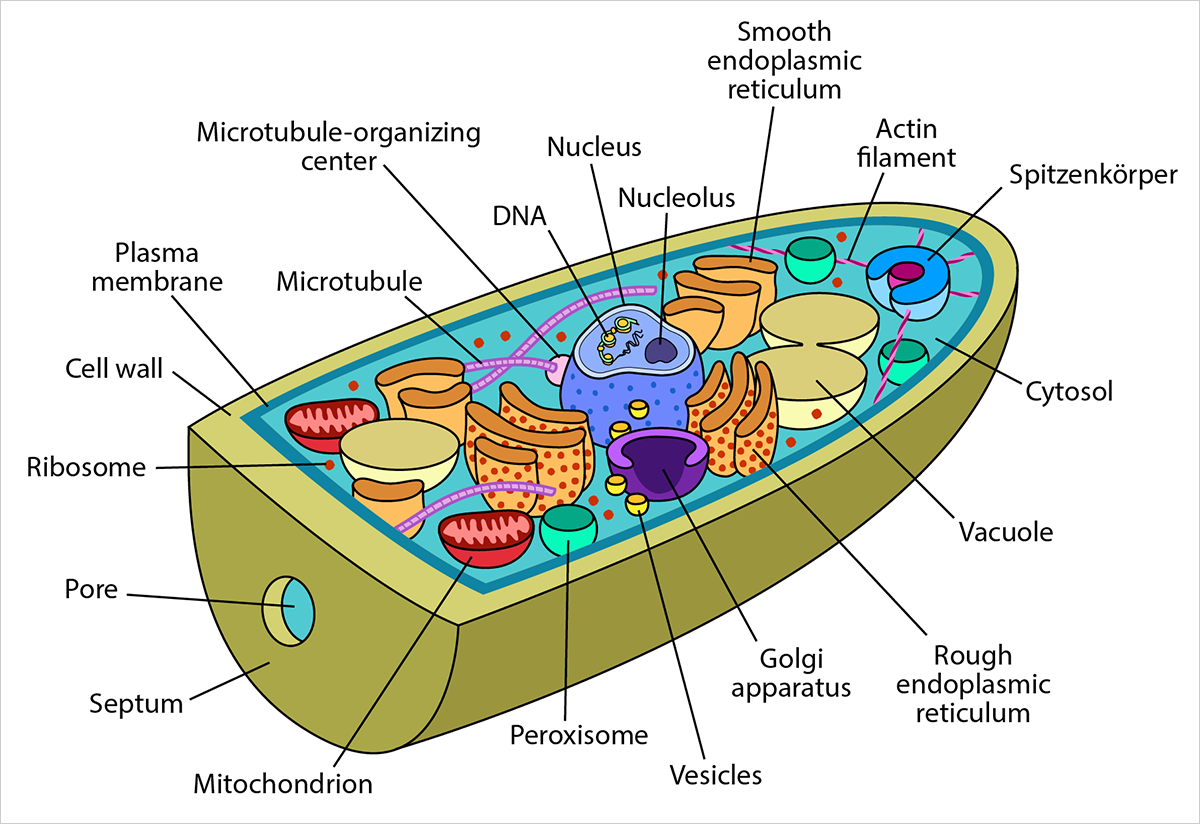
Cell Anatomy Deviche Designs
Cell Structure and Function. Fungi are eukaryotes, and as such, have a complex cellular organization. As eukaryotes, fungal cells contain a membrane-bound nucleus. The DNA in the nucleus is wrapped around histone proteins, as is observed in other eukaryotic cells. A few types of fungi have structures comparable to bacterial plasmids (loops of.
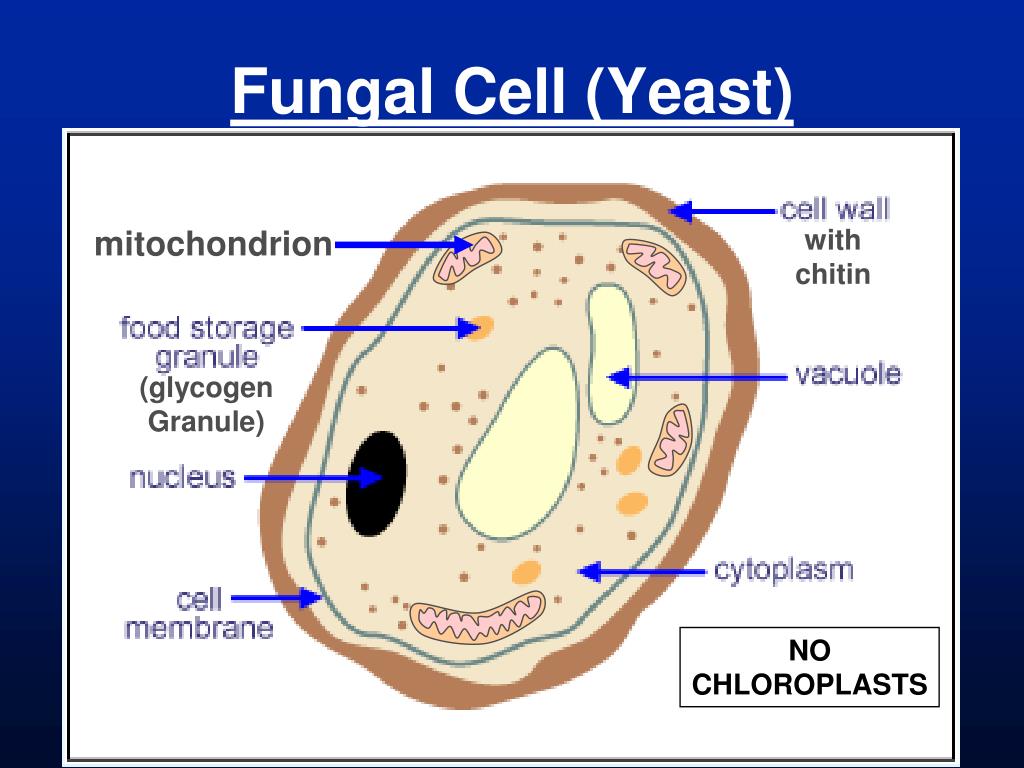
PPT Lab 10. Overview PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID4944026
Human pathogenic fungi produce three basic 'cell' types: hyphae, yeast cells, and spores. The organization and subcellular structure of these different cell types and their modes of growth and formation are reviewed. Growth and form is the consequence of how new cell surface is formed.

Fungi (Importance, Classification and More) Solution Pharmacy
Cell Structure and Function Fungi are eukaryotes and as such have a complex cellular organization.
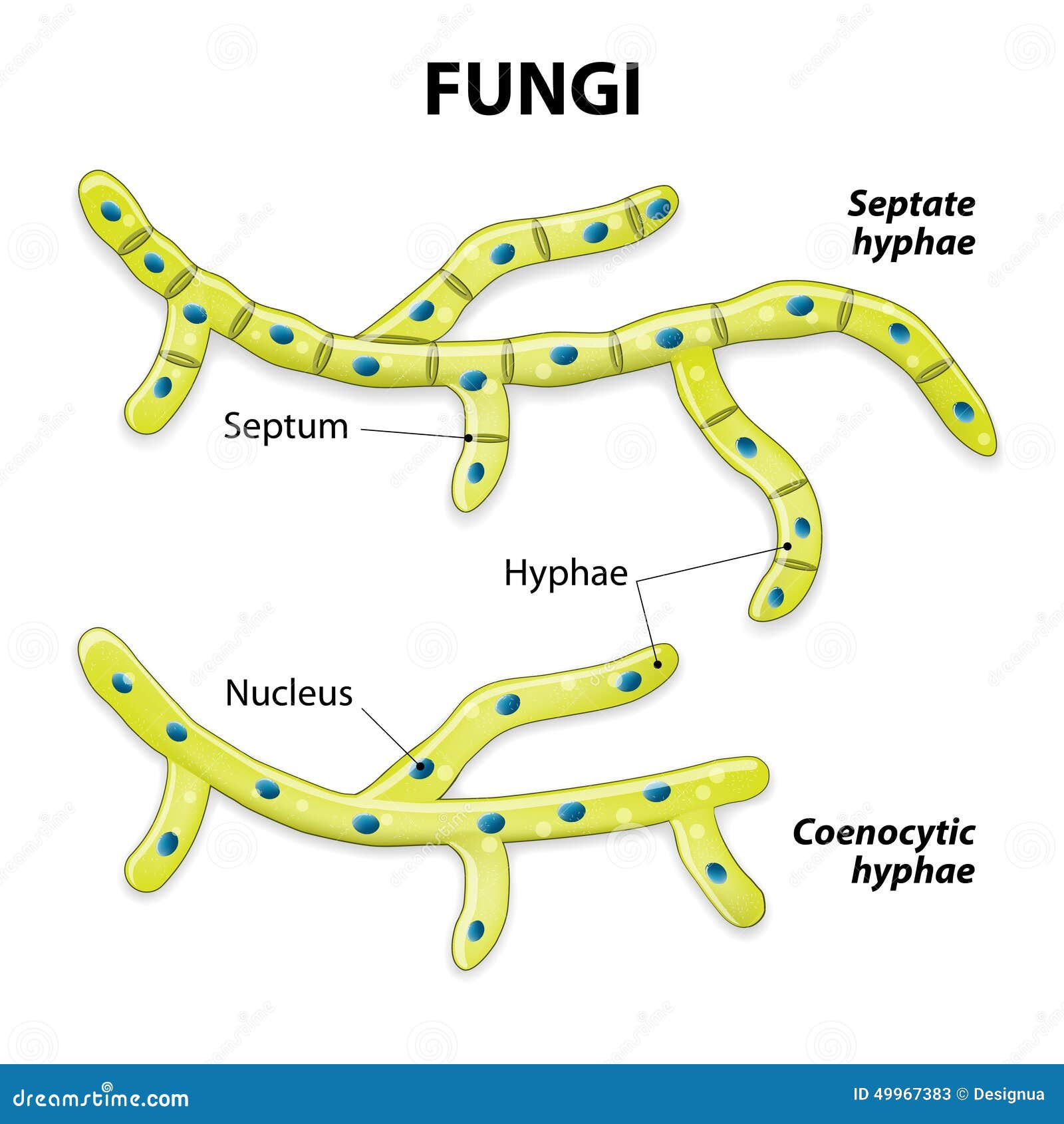
Fungi. Classification Based on Cell Division Stock Vector Illustration of human, multicellular
Cell Structure and Function. Fungi are eukaryotes and have a complex cellular organization. As eukaryotes, fungal cells contain a membrane-bound nucleus where the DNA is wrapped around histone proteins. A few types of fungi have structures comparable to bacterial plasmids (loops of DNA). Fungal cells also contain mitochondria and a complex.

Science Class 5EP
Structure of Fungal Cell (With Diagram) | Fungi Article Shared by ADVERTISEMENTS: In this article we will discuss about the structure of fungal cell. This will also help you to draw the structure and diagram of the fungal cell. (a) The Cell Wall of the Fungal Cell: